Post by 1dave on Jul 11, 2023 9:31:31 GMT -5
Please add what you know to this thread.
Agate is only formed after something shocked an area - Continental collisions, asteroid or comet impact, volcanic H20 explosions, Earthquakes, landslides - That is when silica gel is formed. groundwater caries it and whatever it drug along (yellow, red, or iridescent iron, gold, etc.) into voids, pet wood dino bone . . .
www.geologyin.com/2019/07/what-is-crazy-lace-agate.html
Lace Agate is a variety that exhibits a lace-like pattern with forms such as eyes, swirls, bands or zigzags.
Crazy lace agate is a banded chalcedony (microcrystalline quartz) that's infused with iron and aluminum and is often brightly colored and complexly patterned. This produces the creamy browns, blacks, greys and golds (and occasional pinks or reds) swirled together in this stone.

This stone is found exclusively within the area known as Chihuahua, in Northern Mexico. Crazy lace agate is believed to have been created in the cretaceous period, about 65-90 million years ago.
Agate is the most famous chalcedony variety, recognized by its concentric color bands, formed by the remains of iron and manganese. The chemical composition of agate is the same as quartz, but with a different physical structure.
www.geologyin.com/2018/05/what-is-faden-quartz-and-how-does-it.html
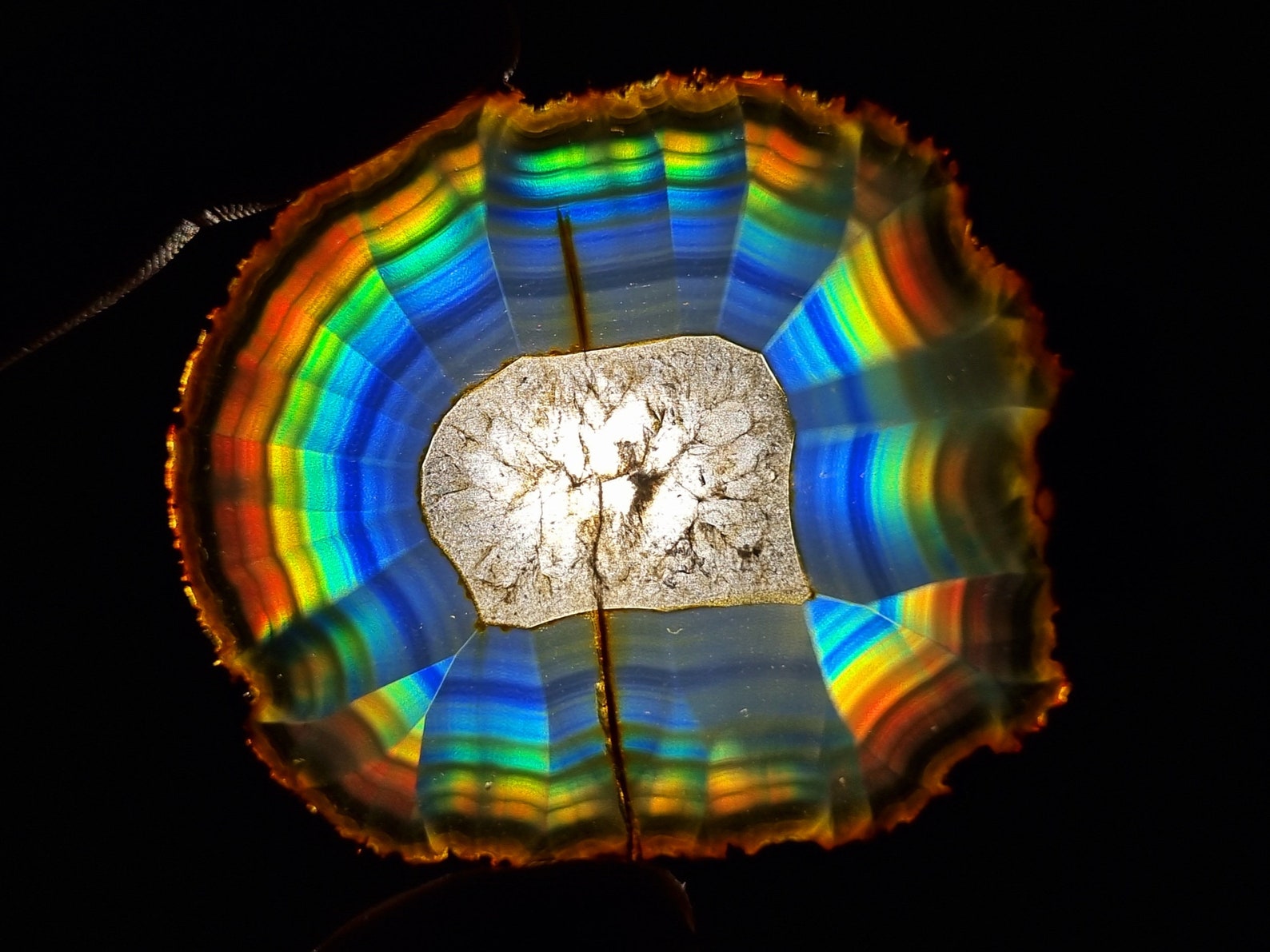
Faden quartz is a descriptive term for a usually tabular group of quartz crystals with a white thread-like or string-like zone running through the interior. The term faden is a German word for "thread". They are found in the Alpine region of Europe, Pakistan, Russia and Arkansas.

They are found in areas of low grade metamorphism in which cavities in the rock are growing. When these zones grow, the quartz crystals in them are broken (repeatedly), and the healing and regrowth incorporates fluid and gaseous inclusions ( the white threads). The edges of the crystals grow faster and incorporate the liquid inclusions in the center of the crystals.
www.geologyin.com/2019/06/what-is-fire-agate.html
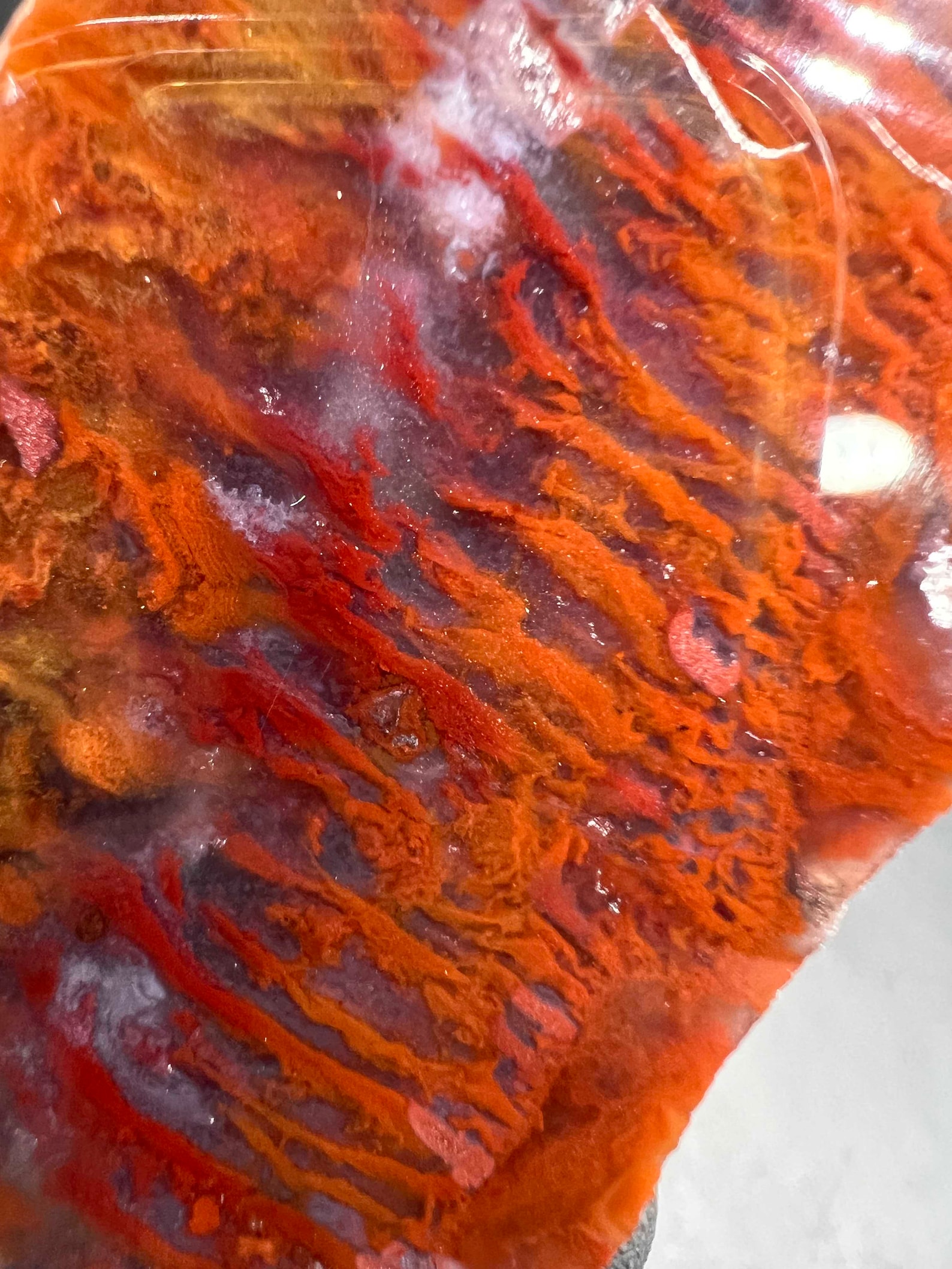
Fire agate is a type of chalcedony, a microcrystalline variety of quartz. It is characterized by its vibrant, iridescent colors, which are caused by the presence of thin layers of iron oxide and other minerals. Fire agates can be found in a variety of colors, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and purple.
Fire Agate is a semi-precious gemstone formed by relatively recent volcanic activity. It is outwardly similar in appearance to quartz, but also shows interesting swirls, bubbles and patterns.
Fire agate is a natural gemstone discovered so far only in certain areas of central and northern Mexico and the southwestern United States (New Mexico, Arizona and California).
Fire agates have beautiful iridescent rainbow colors, similar to opal, with a measurement of hardness on the Mohs scale of between 5 and 7 which reduces the occurrence of scratching when polished gemstones are set in jewelry.
.webp)
Fire agate by Photographer Thomas Shearer
The vibrant iridescent rainbow colors found within fire agates, created by the Schiller effect as found in mother-of-pearl, is caused by the alternating silica and iron oxide layers which diffract and allow light to pass and form an interference of colors within the microstructure layering of the stone causing the fire effect for which it is named.

Agate is only formed after something shocked an area - Continental collisions, asteroid or comet impact, volcanic H20 explosions, Earthquakes, landslides - That is when silica gel is formed. groundwater caries it and whatever it drug along (yellow, red, or iridescent iron, gold, etc.) into voids, pet wood dino bone . . .
www.geologyin.com/2019/07/what-is-crazy-lace-agate.html
Lace Agate is a variety that exhibits a lace-like pattern with forms such as eyes, swirls, bands or zigzags.
Crazy lace agate is a banded chalcedony (microcrystalline quartz) that's infused with iron and aluminum and is often brightly colored and complexly patterned. This produces the creamy browns, blacks, greys and golds (and occasional pinks or reds) swirled together in this stone.

This stone is found exclusively within the area known as Chihuahua, in Northern Mexico. Crazy lace agate is believed to have been created in the cretaceous period, about 65-90 million years ago.
Agate is the most famous chalcedony variety, recognized by its concentric color bands, formed by the remains of iron and manganese. The chemical composition of agate is the same as quartz, but with a different physical structure.
www.geologyin.com/2018/05/what-is-faden-quartz-and-how-does-it.html
Faden quartz is a descriptive term for a usually tabular group of quartz crystals with a white thread-like or string-like zone running through the interior. The term faden is a German word for "thread". They are found in the Alpine region of Europe, Pakistan, Russia and Arkansas.

They are found in areas of low grade metamorphism in which cavities in the rock are growing. When these zones grow, the quartz crystals in them are broken (repeatedly), and the healing and regrowth incorporates fluid and gaseous inclusions ( the white threads). The edges of the crystals grow faster and incorporate the liquid inclusions in the center of the crystals.
www.geologyin.com/2019/06/what-is-fire-agate.html
Fire agate is a type of chalcedony, a microcrystalline variety of quartz. It is characterized by its vibrant, iridescent colors, which are caused by the presence of thin layers of iron oxide and other minerals. Fire agates can be found in a variety of colors, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and purple.
Fire Agate is a semi-precious gemstone formed by relatively recent volcanic activity. It is outwardly similar in appearance to quartz, but also shows interesting swirls, bubbles and patterns.
Fire agate is a natural gemstone discovered so far only in certain areas of central and northern Mexico and the southwestern United States (New Mexico, Arizona and California).
Fire agates have beautiful iridescent rainbow colors, similar to opal, with a measurement of hardness on the Mohs scale of between 5 and 7 which reduces the occurrence of scratching when polished gemstones are set in jewelry.
.webp)
Fire agate by Photographer Thomas Shearer
The vibrant iridescent rainbow colors found within fire agates, created by the Schiller effect as found in mother-of-pearl, is caused by the alternating silica and iron oxide layers which diffract and allow light to pass and form an interference of colors within the microstructure layering of the stone causing the fire effect for which it is named.