Post by 1dave on Sept 2, 2018 7:01:11 GMT -5
cabezaprieta.org/geology.php
cabezaprieta.org/geology/scarborough/index.php
GEOLOGICAL HISTORY OF THE SOUTHWEST
by Bob Scarborough
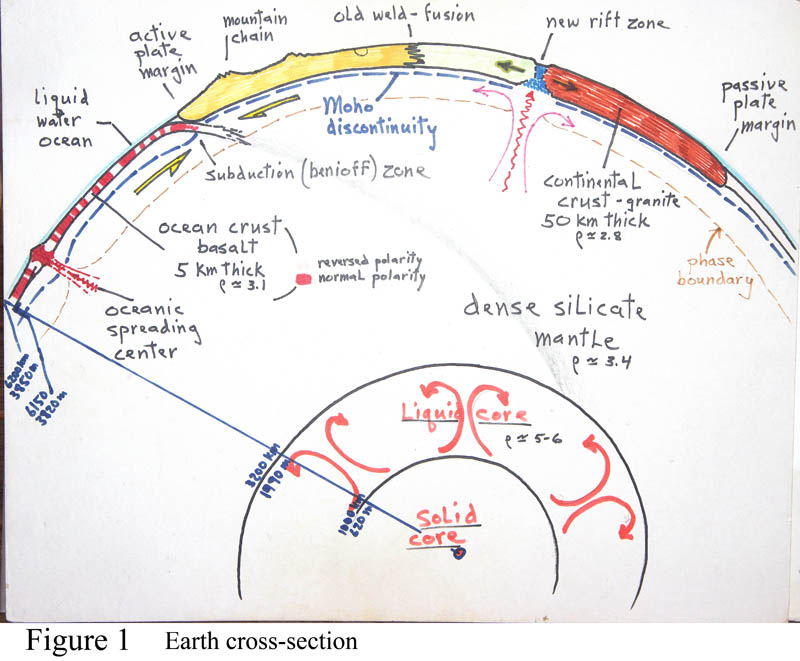
Figure 2: Geological time scale 4 Eons of time
4,560 m.y. ago -- accretion of the solar system; the Earth melts
Hadean Eon -- no rocks preserved
- 3,800 m.y. -- the surface cools; begin continental growth
Archean Eon -- a bunch of small granite 'islands' appear and move about
- 2,500 m.y. -- good signs of oxygen in the atmosphere
Proterozoic Eon -- Rodinia supercontinent, vast cyclic changes
- 550 m.y. -- vast surge of new life forms; continents take shape
Phanerozoic Eon
- Paleozoic Era (550-250 m.y.)
- Mesozoic Era (250-65 m.y.) -- era of the dinosaurs
-- Triassic Period (250-200 m.y.) -- first dinos & mammals @ 225 m.y.
-- Jurassic Period (200-150 m.y.) -- biggest dino ever - Seismosaurus
-- Cretaceous Period (150-65 m.y.) -- Pangea forms up at the end
Cenozoic Era (65 m.y. to modern) -- era of the mammals
-- Paleocene Period (65-56 m.y.)
-- Eocene Period (56-39 m.y.)
-- Oligocene Period (39-23 m.y.)
-- Miocene Period (23-5.5 m.y.)
-- Pliocene Period (5.5-2.4 m.y.)
Pleistocene Period (last 2.4 m.y.)
-- Holocene Epoch (last 10,000 years)
--- Today -- hi-rise condos, café lattes, wars, Degas & Picasso, speeding tickets
(one billion years = 1,000 million years. Millions of years is abbreviated m.y.)
cabezaprieta.org/geology/scarborough/index.php
GEOLOGICAL HISTORY OF THE SOUTHWEST
by Bob Scarborough
Table of Contents:
Introduction
1. Cross-section of Planet Earth
2. Geological time scale
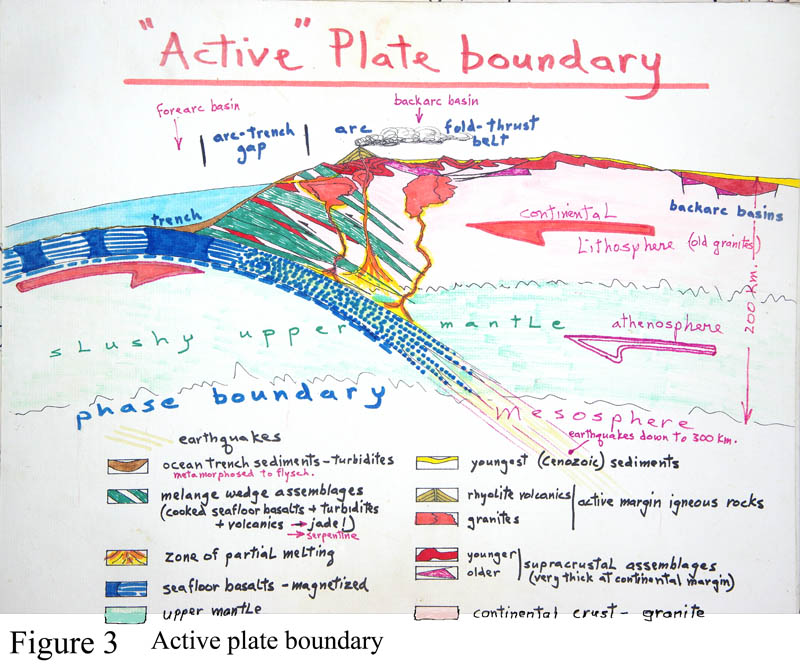
3. An active plate boundary (cross-section)
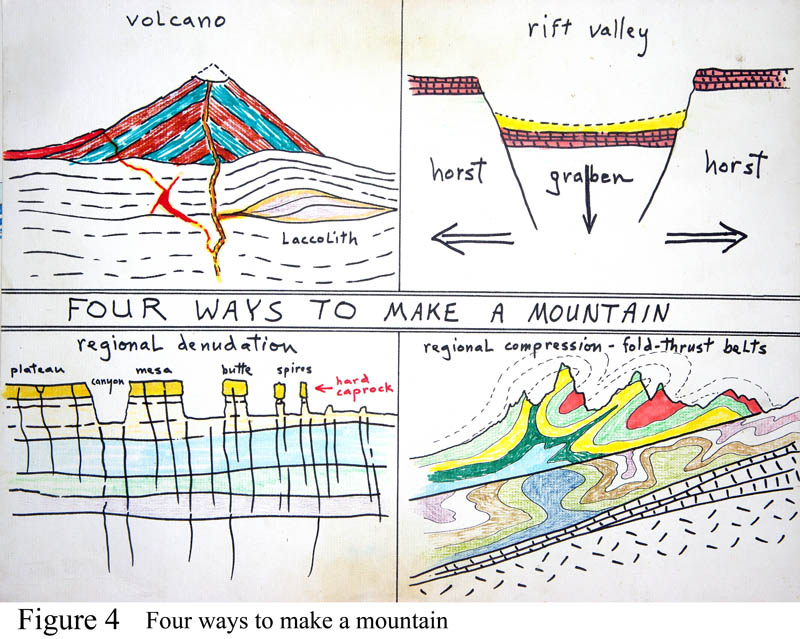
4. Four ways to make a mountain
5. Breakup of Pangea supercontinent
6. Formation of basement terrain of the Southwest
7. Ages of Construction of North America
8 & 9. Maps of Rodinia supercontinent
10. Paleozoic time in North America
11 & 12. Paleozoic layers in Grand Canyon region
13 & 14. North America during the Jurassic period
15 & 16. Arizona in mid-Cretaceous time
17. Southwest in latest Cretaceous time
18. Asteroid strike in the Yucatan
19. Map of Tucson mountains supervolcano
20. Northern Arizona during Eocene wet climate
21 & 22. Cenozoic volcanism in Arizona
23, 24, 25 & 26. Basin and Range Development
27. Modern regional drainage basins
28. Gila River antecedent path
29. Temperature and climate history
30. Geologic Map of southeastern Arizona
31. Topographic map of Arizona, computer-generated
32. Life on Earth flow chart
Major Faults of Southern California
Books of Interest
Acknowledgements
Index of Geologic Terms
Index of Pages
Introduction
1. Cross-section of Planet Earth
2. Geological time scale
3. An active plate boundary (cross-section)
4. Four ways to make a mountain
5. Breakup of Pangea supercontinent
6. Formation of basement terrain of the Southwest
7. Ages of Construction of North America
8 & 9. Maps of Rodinia supercontinent
10. Paleozoic time in North America
11 & 12. Paleozoic layers in Grand Canyon region
13 & 14. North America during the Jurassic period
15 & 16. Arizona in mid-Cretaceous time
17. Southwest in latest Cretaceous time
18. Asteroid strike in the Yucatan
19. Map of Tucson mountains supervolcano
20. Northern Arizona during Eocene wet climate
21 & 22. Cenozoic volcanism in Arizona
23, 24, 25 & 26. Basin and Range Development
27. Modern regional drainage basins
28. Gila River antecedent path
29. Temperature and climate history
30. Geologic Map of southeastern Arizona
31. Topographic map of Arizona, computer-generated
32. Life on Earth flow chart
Major Faults of Southern California
Books of Interest
Acknowledgements
Index of Geologic Terms
Index of Pages

Figure 2: Geological time scale 4 Eons of time
4,560 m.y. ago -- accretion of the solar system; the Earth melts
Hadean Eon -- no rocks preserved
- 3,800 m.y. -- the surface cools; begin continental growth
Archean Eon -- a bunch of small granite 'islands' appear and move about
- 2,500 m.y. -- good signs of oxygen in the atmosphere
Proterozoic Eon -- Rodinia supercontinent, vast cyclic changes
- 550 m.y. -- vast surge of new life forms; continents take shape
Phanerozoic Eon
- Paleozoic Era (550-250 m.y.)
- Mesozoic Era (250-65 m.y.) -- era of the dinosaurs
-- Triassic Period (250-200 m.y.) -- first dinos & mammals @ 225 m.y.
-- Jurassic Period (200-150 m.y.) -- biggest dino ever - Seismosaurus
-- Cretaceous Period (150-65 m.y.) -- Pangea forms up at the end
Cenozoic Era (65 m.y. to modern) -- era of the mammals
-- Paleocene Period (65-56 m.y.)
-- Eocene Period (56-39 m.y.)
-- Oligocene Period (39-23 m.y.)
-- Miocene Period (23-5.5 m.y.)
-- Pliocene Period (5.5-2.4 m.y.)
Pleistocene Period (last 2.4 m.y.)
-- Holocene Epoch (last 10,000 years)
--- Today -- hi-rise condos, café lattes, wars, Degas & Picasso, speeding tickets
(one billion years = 1,000 million years. Millions of years is abbreviated m.y.)













