Post by 1dave on Sept 25, 2018 17:59:41 GMT -5
Triassic Times - Beginning of the Age of the Dinosaurs.
Named after the three distinct rock layers that are found throughout Europe in 1834 by Friedrich von Alberti.
1. The lower red beds (Moenkopi - named for a Hopi village) were a desolate time in Earth's history. Violent volcanic eruptions, climate change, dust from a major impact had just triggered the extinction of more than 90 percent of Earth's species.
2. The middle white limestones were a time of tremendous change and rejuvenation. Life that survived the Great Dying repopulated the planet, diversified into freshly exposed ecological niches, and gave rise to new creatures, including rodent-size mammals and the first dinosaurs.
3. The upper terrestrial brown mud and sandstones differentiate the soils after a new extinction event that began during the Late Triassic. Not as destructive as the preceding Permian Period which took place approximately 50 million years earlier, it still resulted in the disappearance of about 76% of all terrestrial and marine life species.
Moenkopi - I searched the internet for the meaning. As it was not given anywhere, I finally searched for it in a Hopi Dictionary. The nearest I could come for Moen is mohpe - in front; mong'aqvi - front part; and kopi - koopa'at - top of head, center whirl; and Kopatsoki - headdress.
My best guess: Front top of head or hair whirl.
The Moenkopi Formation preserves extensive ancient tidal and near shore deposits. Continental conditions were located to the east, and marine conditions to the west. Mostly devoid of life, It is spread across the U.S. states of southeastern California, Nevada, eastern Utah, western Colorado, northern Arizona, and New Mexico.
This unit is considered to be a group in Arizona.
Part of the Colorado Plateau and Basin and Range, this marine and tidal flat land of red silt, mudstone, sandstone and clay was laid down in the Lower Triassic and possibly part of the Middle Triassic, around 240 million years ago.
Originally about 2,000 feet thick, most of it was uplifted and removed during the Cretaceous Sevier Orogeny.
Fossil sedimentary features demonstrate flood plains, wandering stream channels, and shallow seas. Beds of gypsum and casts of salt cubes suggest long periods of evaporation.
A few tracks and skeletons of large amphibians in the deposits indicate warm climates.
The bottom layer, the Black Dragon Member, is followed by the Sinbad Limestone Member, then the overlying Torrey Member. The final member, The Moody Canyon Member, was deposited under widespread, low-energy marine conditions, producing a generally "structure-less" mudstone. (Blakey, 1973)

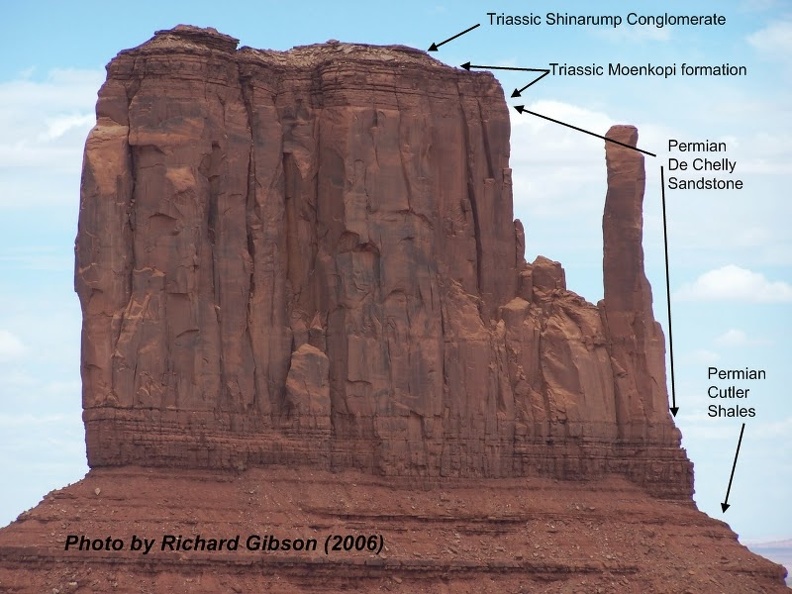
The Triassic Moenkopi is on top of Permian De Chelly Sandstone in Monument Valley.



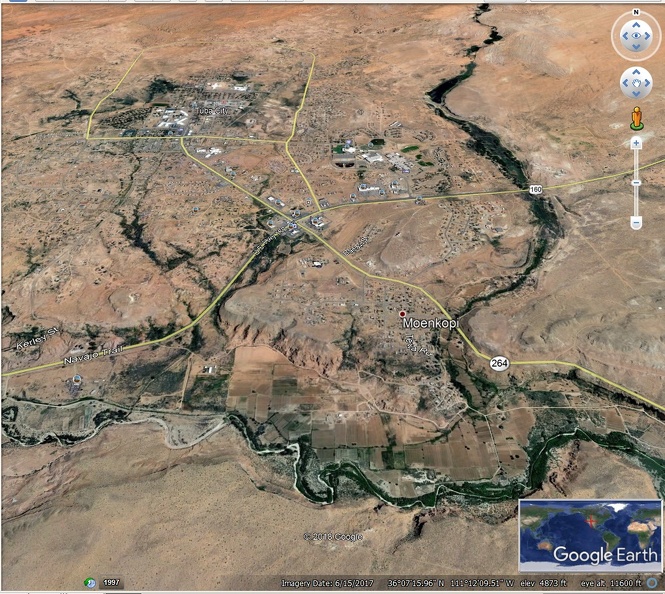
The village of Moenkopi is about 80 miles north of Flagstaff Arizona, and two miles southeast of Tuba City.


The main stopping place is between Moenkopi and Tuba City.





Named after the three distinct rock layers that are found throughout Europe in 1834 by Friedrich von Alberti.
1. The lower red beds (Moenkopi - named for a Hopi village) were a desolate time in Earth's history. Violent volcanic eruptions, climate change, dust from a major impact had just triggered the extinction of more than 90 percent of Earth's species.
2. The middle white limestones were a time of tremendous change and rejuvenation. Life that survived the Great Dying repopulated the planet, diversified into freshly exposed ecological niches, and gave rise to new creatures, including rodent-size mammals and the first dinosaurs.
3. The upper terrestrial brown mud and sandstones differentiate the soils after a new extinction event that began during the Late Triassic. Not as destructive as the preceding Permian Period which took place approximately 50 million years earlier, it still resulted in the disappearance of about 76% of all terrestrial and marine life species.
Moenkopi - I searched the internet for the meaning. As it was not given anywhere, I finally searched for it in a Hopi Dictionary. The nearest I could come for Moen is mohpe - in front; mong'aqvi - front part; and kopi - koopa'at - top of head, center whirl; and Kopatsoki - headdress.
My best guess: Front top of head or hair whirl.
The Moenkopi Formation preserves extensive ancient tidal and near shore deposits. Continental conditions were located to the east, and marine conditions to the west. Mostly devoid of life, It is spread across the U.S. states of southeastern California, Nevada, eastern Utah, western Colorado, northern Arizona, and New Mexico.
This unit is considered to be a group in Arizona.
Part of the Colorado Plateau and Basin and Range, this marine and tidal flat land of red silt, mudstone, sandstone and clay was laid down in the Lower Triassic and possibly part of the Middle Triassic, around 240 million years ago.
Originally about 2,000 feet thick, most of it was uplifted and removed during the Cretaceous Sevier Orogeny.
Fossil sedimentary features demonstrate flood plains, wandering stream channels, and shallow seas. Beds of gypsum and casts of salt cubes suggest long periods of evaporation.
A few tracks and skeletons of large amphibians in the deposits indicate warm climates.
The bottom layer, the Black Dragon Member, is followed by the Sinbad Limestone Member, then the overlying Torrey Member. The final member, The Moody Canyon Member, was deposited under widespread, low-energy marine conditions, producing a generally "structure-less" mudstone. (Blakey, 1973)

The Triassic Moenkopi is on top of Permian De Chelly Sandstone in Monument Valley.



The village of Moenkopi is about 80 miles north of Flagstaff Arizona, and two miles southeast of Tuba City.


The main stopping place is between Moenkopi and Tuba City.

















